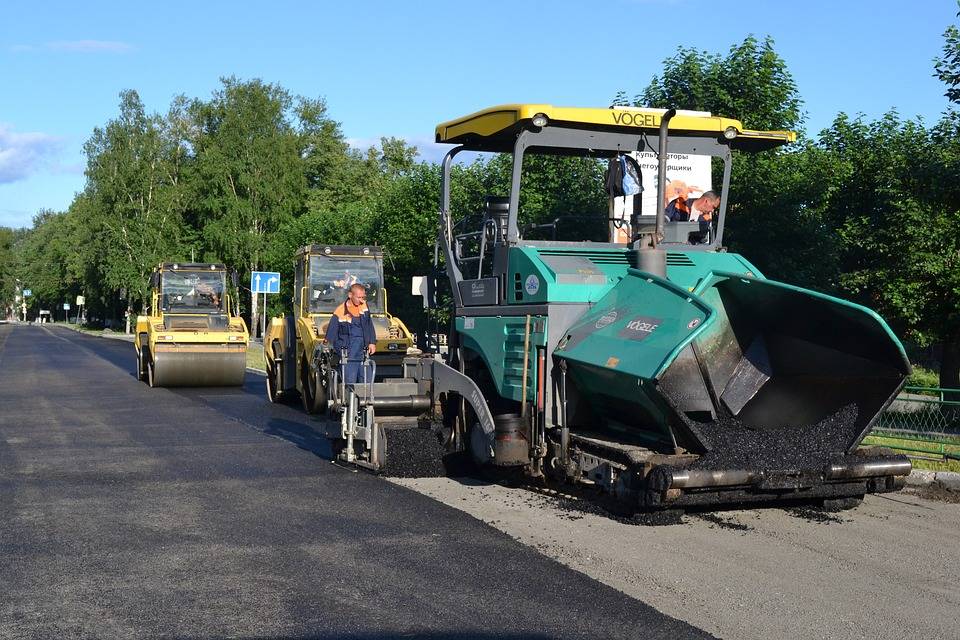
Bitumen Production. Various types of crude oil are used for production of bitumen, and all the process occurs at refineries.
The process of oil refining includes fraction distillation, which results in the production of light oil products, such as gasoline, kerosene, ligroin, lubricants etc. After removal of lighter fractions, oil residue remains which is then used to make bitumen.
There are several methods of bitumen production:
- Concentration of oil residue by vacuum distillation in the presence of water vapor or inert gas – non-oxidized bitumen. Residual bitumen is a low viscosity product and is usually susceptible to oxidation;
- Blowing of the various oil residue with air oxygen (tower bottoms, tar deasphaltation asphalts, heavy oil, extracts of selective oil purification, cracking residue and mixes) – at high temperature – oxidized bitumen;
- Mixing of various bitumens – compounded bitumen.
Non-oxidized bitumen is made by vacuum distillation of oil residue and heavy oil. The raw material must have a high concentration of tar and asphalt.
Oxidized bitumen is 75-80% of the total amount of the total amount of bitumen made in the world. Oxidized bitumen is made in batch distillers and in coil type reactors.
Non-oxidized and compounded bitumens have a high content of heavy aromatics and tar, and demonstrate good adhesion, high elasticity, but at the cost of a higher brittle temperature.
Research shows that cracking resistance of asphalt made with non-oxidized and compounded bitumen is significantly higher than that of mixes of similar composition but with oxidized bitumen.
Non-oxidized and compounded bitumens after treatment demonstrate high residual penetration, elasticity and adhesion, that is, the properties of the bitumen remain at the same high level, and the difference between the parameters of oxidized and non-oxidized bitumen increases.